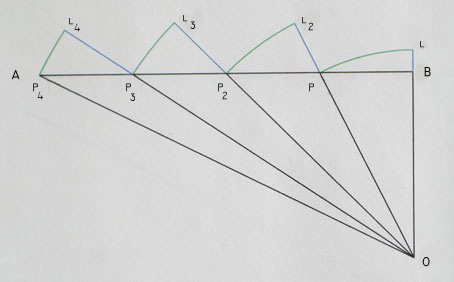

OB = 1
BA is a straight line perpendicular to OB
OA = L
BA = X
If the number of segments between B and A are doubled, then the sum of the perpendicular segments (y-length) is slightly less than the sum for the previous diagram. If the segments are increased ad infinitum then the y-length is defined by the equation below.
perpendicular distance [y-length] = ln (L + X)
If the segments between B and A are doubled, the sum of the linear segments [x-length] are the same as in the previous diagram. The amount is the same regardless of the number of segments.
linear distance [x-length] = L - 1
in the diagram:
AB = 1.959592
AO = 2.2
y-length of BA, relative to O, is:
y-length = ln(1.959592 + 2.2)
y-length = 1.425417
x-length of BA, relative to O, is:
x-length = 2.2 - 1
x-length = 1.2