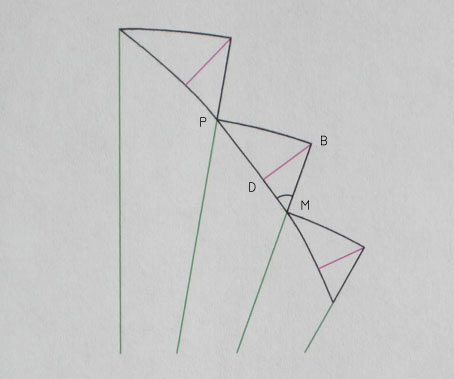

In the diagram, the length BD represents the h-length
segment of MP, which is part of a log spiral. This distance is equal
to the x-length (MB) multiplied by the Sin at M (angle BMD). The
Sin at M being equal to the Cos(s), and these two values being
constant everywhere on the curve, the h-length between any two
points is the product of the x-length between those points and
the value of the Cos(s).
In a log spiral the h-length, from any point on the
curve to the origin at O, relative to O, equals the distance of the ray L drawn
from the point to the origin, multiplied by the value of the Cos(s).
h-length = L(Cos s)
The h-length between any two points on the curve, relative to O, is the difference between the two rays, drawn from the origin to each separate point, multiplied by the Cos(s).
h-length = (L - L2 )Cos s
in the diagram:
L = e(.9)θ
OP = L = 4.537856
OM = L2 = 4.363323
Cos(s) = .725476
the h-length from P to the origin at O, relative to O, is
h-length = 4.537856(.725476)
= 3.292105
the h-length from P to M, relative to O, is
h-length = (4.537856 - 4.363323).725476
= .126619